Single-Sided Rigid PCB: The Foundation of Reliable Electronics
2025-05-06
The Single-Sided Rigid PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is one of the most fundamental types of circuit boards used in electronic devices. Despite its simplicity, it plays a crucial role in various applications, from household appliances to industrial equipment. As the name suggests, a single-sided rigid PCB features components mounted only on one side of a rigid substrate, offering an efficient, cost-effective, and reliable solution for many electronic designs.
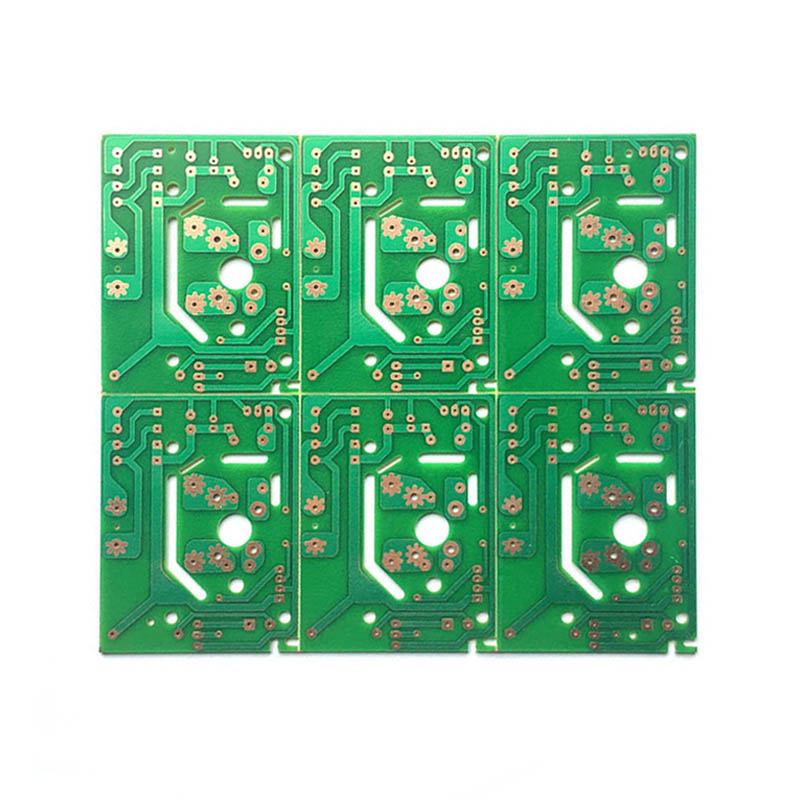
What Is a Single-Sided Rigid PCB?
A Single-Sided Rigid PCB is a type of printed circuit board where all the components are placed on one side, with the opposite side being used for conductive pathways. The board is rigid, meaning it is made from a solid material such as fiberglass or epoxy resin that ensures structural stability. This type of PCB is the most basic form of PCB, with a single layer of conductive material (typically copper) for the electrical connections.
Key Features
1. Single Layer of Conductive Material
The board is typically copper-plated on one side, with the circuit traces etched or printed on the surface.
2. Component Placement on One Side
All the electronic components (resistors, capacitors, diodes, etc.) are placed on one side of the PCB.
3. Rigid Construction
Made from materials like fiberglass (FR4), this type of PCB is strong and provides a stable, non-flexible platform for the components.
4. Simple Design
Compared to more complex PCBs, single-sided rigid PCBs have a straightforward design, making them easier and less costly to manufacture.
5. Low Density
They are best suited for simple electronic circuits with fewer components.
Advantages of Single-Sided Rigid PCBs
1. Cost-Effective
Since the design is simple and requires fewer materials, single-sided rigid PCBs are relatively inexpensive to produce, making them a great option for budget-conscious projects.
2. Ease of Manufacturing
The simple one-sided design makes them easier to fabricate, reducing lead time and manufacturing complexity.
3. Compact and Durable
The rigid construction ensures that the PCB can withstand external forces, providing a durable and reliable foundation for electronic components.
4. Simplified Troubleshooting
With fewer layers and components, it’s easier to troubleshoot and test the circuits during the development phase.
5. Ideal for Low-Complexity Circuits
These PCBs are perfectly suited for less complicated electronic devices where the need for advanced connectivity and compact designs is minimal.
Common Applications
Single-Sided Rigid PCBs are found in a wide range of applications, especially where cost and simplicity are key factors. Some typical uses include:
Consumer Electronics: Radios, televisions, and basic gadgets
Home Appliances: Microwaves, washing machines, and refrigerators
Automotive: Simple car control systems and dashboard electronics
Toys and Small Devices: Toys, remote controls, and calculators
Industrial Equipment: Basic control panels and monitoring systems
Limitations of Single-Sided Rigid PCBs
While single-sided rigid PCBs have many advantages, they do have certain limitations:
Limited Component Density: As they can only accommodate components on one side, they are not suitable for highly complex circuits with a large number of components.
Limited Routing Options: The single layer of conductive traces limits the complexity of the routing, making it unsuitable for designs that require many interconnections.
Conclusion
A Single-Sided Rigid PCB remains a popular choice for many electronic devices due to its simplicity, reliability, and low manufacturing cost. It is an ideal solution for applications that do not require advanced features like multi-layer circuits or high component density. Whether used in everyday household items or industrial equipment, this basic yet effective circuit board continues to be a cornerstone in the world of electronics.


